Filter and sort
What are surface pumps and what are they used for?
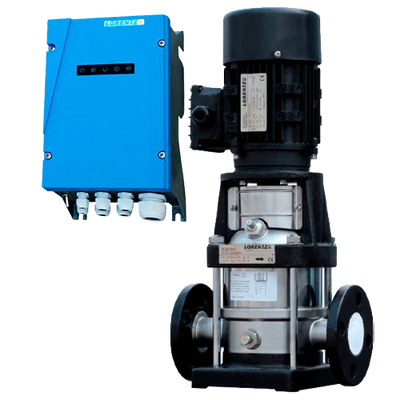
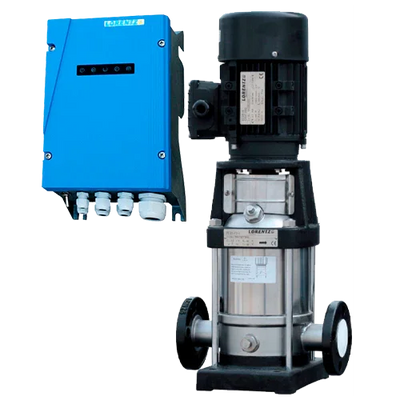
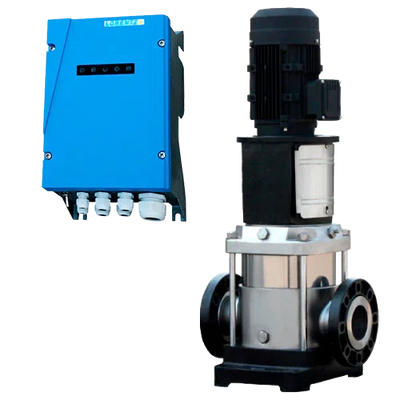
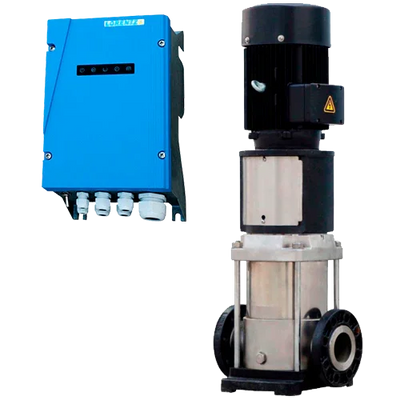
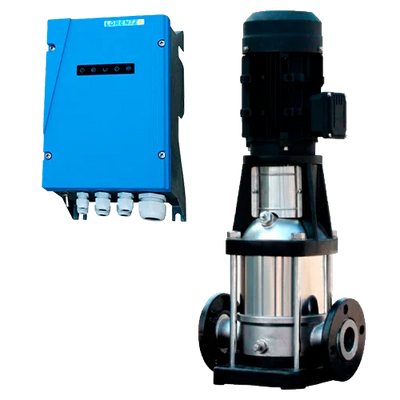
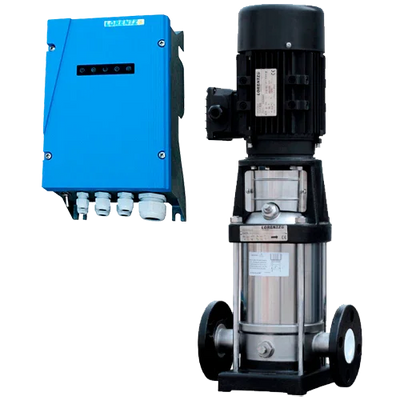
Surface pumps are devices installed outside the water that draw from a suction point (tank, chamber, channel) and deliver flow and pressure to the discharge. They allow for transfers, irrigation, tank filling, and local pressurization without the need to submerge the pump in the fluid. In our catalog you will find solar solutions (Lorentz PS2 CS-F, ZIRI DCP), hybrid and AC models (ZIRI CPM/QB/SHF), covering from small flows to high-flow and medium-head applications. In Lorentz, the PS2 series includes an MPPT controller; PU units without a controller are managed as spare parts.
Advantages and limitations
- Easy maintenance: immediate access to the equipment for inspection, cleaning, and replacement.
- Energy versatility: operation with direct solar (MPPT), 12/24/48 V DC or 230 V AC.
- Wide range: high-flow models and BOOST versions for greater heads.
- Limitations: suction head is limited; it is recommended to install the pump as close to and below the water level as possible to facilitate priming. If the intake is very deep, consider submersible pumps.
Common applications
- Transfers between tanks, ponds, and containers.
- Irrigation (drip/sprinkler) from tanks or surface watercourses.
- Local pressurization of circuits (wash areas, hoses, auxiliary lines).
- Supply to swimming pool filtration units (solar/hybrid depending on configuration).
How to choose your surface pump
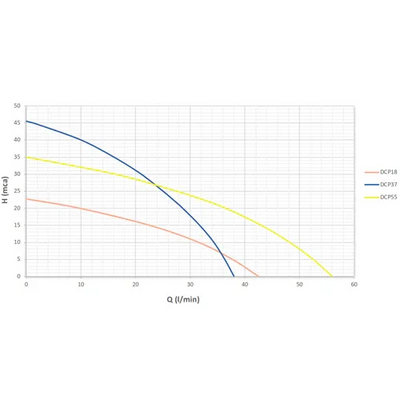
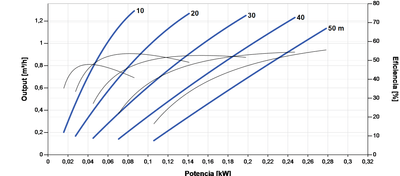
- Operating point: define flow (m³/h) and Total Manometric Head (TMH, m) = static head + losses (piping, elbows, valves, filters). Check that the flow–head curve of the model crosses your operating point with margin.
- Power source: solar with MPPT (PS2 already integrates it), 12/24/48 V DC for battery systems, or 230 V if grid/inverter is available.
- Hydraulics: centrifugal CS-F/CPM/QB for medium/high flows and low–medium heads; BOOST versions for higher heads with moderate flows.
- Water quality: if there are sediments, install a filter and strainer on the suction side to protect the impeller and seal.
- Control and protection: pressure switch/press-control if supplying an internal network; dry run (floats/sensors) and check valve on the discharge.
Indicative specifications
| Typical flow | 0.25–57 m³/h depending on series (CS-F, CPM, QB, SHF, BOOST) |
| Manometric head | 10–150 m (up to 150 m in BOOST models) |
| Power supply | Solar MPPT / 12–24–48 V DC / 230 V AC |
| Hydraulics | Centrifugal (general services) | High pressure (BOOST) |
| Control | Integrated MPPT (PS2), pressure switch/press-control, variable speed drive depending on model |
| Protections | Foot valve and strainer on suction, check valve on discharge, dry run, DC overvoltage |
Best installation practices
- Place the pump close to and below the water level whenever possible; minimize suction head and elbows.
- Install a foot valve and strainer on the suction side to maintain priming and prevent solids.
- Use piping of sufficient diameter to reduce losses; avoid long and narrow sections.
- For solar, size the PV array and cables to meet the controller’s voltage/current requirements; respect maximum lengths.
- Maintenance plan: filter cleaning, seal and fitting inspection, valve testing, and electrical protection check.
Comparisons and related accessories
If the water source is deep, a submersible pump will be more suitable. To supply taps and showers from a tank, add a pressure pump. For pool recirculation, visit swimming pool filtration units. Complete the installation with accessories (pressure switches/press-control, valves, filters, and DC/AC protections) and consult spare parts for specific components. Return to the overview at Water Pumps or explore: Solar, Hybrid, and AC.